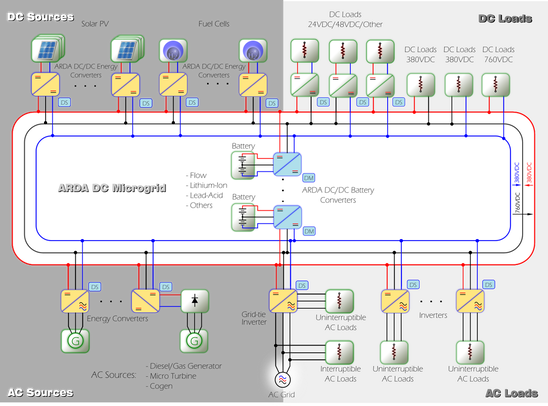
ARDA DC Microgrid Platform
Components: Energy Storage, Loads, Sources, Power Converters
|
Using the ARDA DC Microgrid Platform customers can integrate a wide range of Components on to a microgrid on a “plug and play” basis using third party modular Power Converters.
|
The commands are then communicated to these Components using distributed ARDA Virtual Master Controller and ARDA Response Controllers .
|
Energy Storage |
Energy Storage system plays a central Management role in the ARDA DC Microgrid Platform simultaneously acting as both the Power and the Energy Manager.
PLUG-and-PLAY The Platform's proprietary Controls allow customers to easily scale, add or remove energy storage capacity.
|
Sources |
A DC microgrid is great for DC Sources and the ARDA DC Microgrid Platform is no exception. But that’s not all, many distributed sources of “AC” energy will benefit significantly when linked to a DC microgrid.
The ARDA DC Microgrid Platform promotes modularity in sizing components including Sources, but can also accommodate non-modular approach too.
PLUG-and-PLAY The Platform's proprietary Controls allow customers to easily scale, add or remove energy generation capacity.
|
Source Converters
Sources connect to the bi-polar DC bus using third-party converters that output power at
760VDC (+/- 380VDC).
ARDA Response Controllers are used with third-party converters.
For Solar PV the Source Converters used to connect to the DC bus are capable of managing the maximum power point tracking (MPPT).
It is important in a DC Microgrid application that the Solar Source Converters are able to isolate or significantly reduce ground faults to the DC bus, either with:
- isolated converters (the most resilient and maintenance friendly approach)
- non-isolated converters with ground fault limitation
Loads |
The ARDA DC Microgrid Platform is by definition friendly to DC Loads. In addition, many AC Loads are actually “Camouflaged” DC Loads that will benefit significantly when linked to an ARDA DC Microgrid.
AC Loads For the foreseeable future DC Microgrids will not only have to accommodate regular AC loads, but will often co-exist on the same site or in the same building with traditional local AC distribution networks.
If there is a requirement to have select AC Loads operate during AC Grid faults or outages, or in the case of Off Grid applications, the base option is to connect these loads to the ARDA DC Microgrid Platform via dedicated DC-AC inverters. PLUG-and-PLAY The Platform's proprietary Controls allow customers to easily scale, add or remove Loads.
|
Load Converters
Both "Genuine" and "Camouflaged" DC Loads can be connected directly to the DC bus at
760VDC (+/- 380VDC)
DC Loads with the lower voltages connect to the DC bus via off-the-shelf down (buck) DC-DC Converters.
AC Loads connect to the DC bus by third-party DC-AC inverters.
Add-on ARDA Response Controllers are available as required.
AC Grid |
In the ARDA DC Microgrid Platform, the AC Grid and its interfacing grid tie DC-AC inverter play NO Management role. Instead the AC Grid is simply a bidirectional device that can operate as a Source or a Load on our Platform.
PLUG-and-PLAY The Platform's proprietary Controls allow customers to easily scale, add or remove AC Grid's energy import/export capacity for the Microgrid.
|
Grid tie ConvertersThe ARDA DC Microgrid connects to the grid using third-party grid tie DC-AC converters with a fixed (narrow range) DC input voltage at: |